In the 1990s, the design of feeds for aquaculture didn’t take into account the amount of nutrients that the animal can absorb and utilise
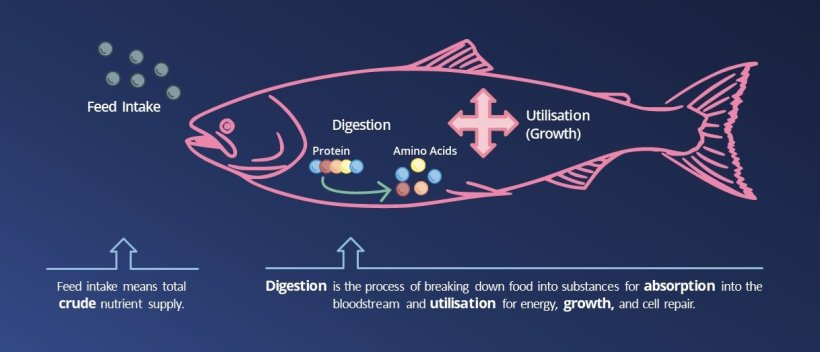
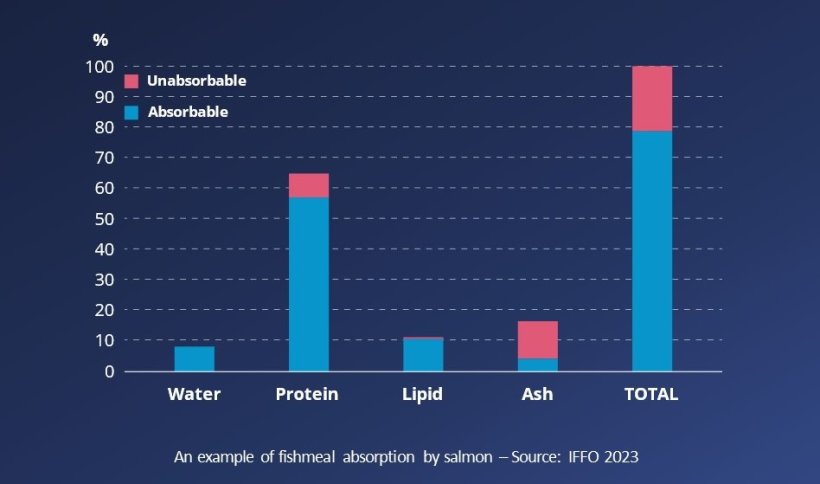
Yet, out of total nutrient supplies ingested by a salmon, only a fraction is absorbed
Today, different feeds are produced for different species and environments based on variable nutrient and energy specifications
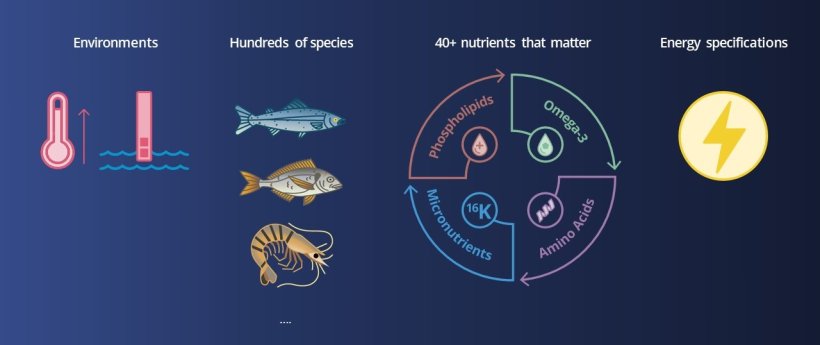
What are the changes made in the feed design depending on these various parameters?

Based on a precision nutrition approach, marine ingredients are being used more strategically, where they leverage greatest value…
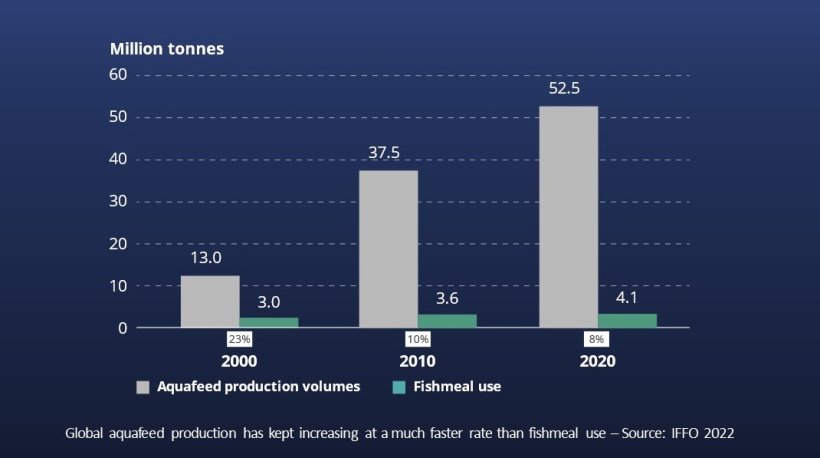
…therefore improving the efficiency of the feeding process, including its environmental footprint

Nutrients are used in a targeted manner throughout life stages.

Sources: Carr, I., Glencross, B., & Santigosa, E. (2023). The importance of essential fatty acids and their ratios in aquafeeds to enhance salmonid production, welfare, and human health. Frontiers in Animal Science, 4, 1147081.
Huyben, D., Grobler, T., Matthew, C., Bou, M., Ruyter, B., & Glencross, B. (2021). Requirement for omega-3 long-chain polyunsaturated fatty acids by Atlantic salmon is relative to the dietary lipid level. Aquaculture, 531, 735805.
Sprague, M., Xu, G., Betancor, M. B., Olsen, R. E., Torrissen, O., Glencross, B. D., & Tocher, D. R. (2019). Endogenous production of n-3 long-chain PUFA from first feeding and the influence of dietary linoleic acid and the α-linolenic: linoleic ratio in Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar). British Journal of Nutrition, 122(10), 1091-1102.
Glencross, B. D. (2009). Exploring the nutritional demand for essential fatty acids by aquaculture species. Reviews in Aquaculture, 1(2), 71-124.
Glencross, B. D., Tocher, D. R., Matthew, C., & Gordon Bell, J. (2014). Interactions between dietary docosahexaenoic acid and other long-chain polyunsaturated fatty acids on performance and fatty acid retention in post-smolt Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar). Fish physiology and biochemistry, 40, 1213-1227.
Bou, M., Berge, G. M., Baeverfjord, G., Sigholt, T., Østbye, T. K., Romarheim, O. H., ... & Ruyter, B. (2017). Requirements of n-3 very long-chain PUFA in Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar L): effects of different dietary levels of EPA and DHA on fish performance and tissue composition and integrity. British Journal of nutrition, 117(1), 30-47.










